Cultivation of Sorghum Plant: Full Guideline
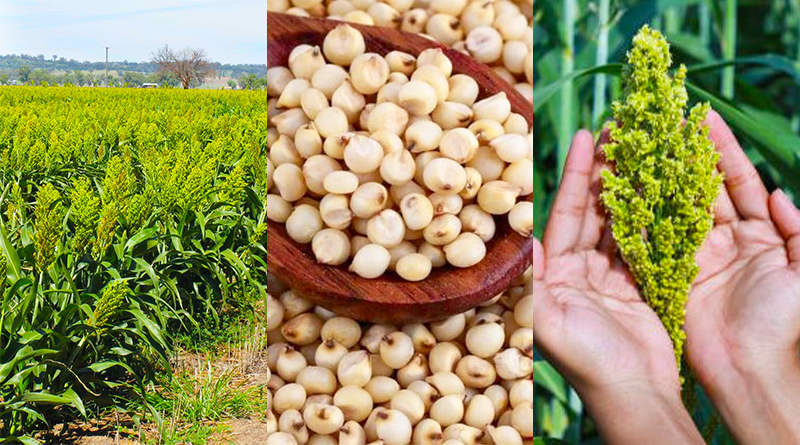
The sorghum plant might be one of the most common and useful cereal crops that many gardeners have never heard. One of the most versatile members of the grass family, sorghum can be grown for grain, crafting or for processing into sorghum syrup. Sorghum is a resilient crop that thrives in hot, dry climates with well-drained soil. Sorghum grows best where summers are quite warm, with daytime temperatures regularly topping 90 °F. It requires moderate watering and can tolerate drought well.
Sorghum Cultivation
Sorghum thrives in areas with long, hot summers. The best time to plant sorghum is when the temperatures are consistently warm, with many gardeners waiting until May or early June. Sow directly in the ground for the best results. Sow seeds one-half inch deep and 4 inches apart, and thin to 8 inches apart when the seedlings are 4 inches tall. Plant sorghum in a warm area in full sun and in well-draining soil.
Keep weeds under control until developing sorghum plants are big enough to dominate their space. Young sorghum plants have difficulty competing with weeds. Six weeks after planting, drench sorghum with a high-nitrogen liquid fertilizer to invigorate new growth. Many grain sorghum varieties grow to only 5 feet tall, but sweet sorghum and broom corn plants can top 8 feet.
Harvesting
If you’re growing sweet sorghum to produce sorghum syrup, cut the stalks down at the base about two weeks after the ‘milk’ stage like corn. If you’re growing grain sorghum, wait until the seeds are fully developed on the plant. Once the seeds are hard and glossy, they are ready to be harvested. Cut off the top portions of the stalk with the seed heads still attached and leave them in a warm place to dry for at least a week.
87 total views, 1 views today




Pingback:Agriculturelearning-The biggest field of agricultural information in Bangladesh